 |
4 steps : natel A : 78 analogical
160 Mhz
natel B : 80 analogical 160
Mhz
natel C : 87 analogical 900
Mhz
natel D : 93 digital 900 Mhz
natel E : 96 digital 1800 Mhz
Inmarsat digital 1600 Mhz
Head office in Vaud : Unisource
Mobile/rue Sebeillon 1/ Lausanne
21/05/93
16/53 PARLAMENTSDIENSTE ZS 3003 BERN 002
1. Is the federal Council ready to thwart the increasing efforts of the people and the tax authorities, of the political police and the secret service which illegally carry out phone-tapping operations in order to collect information?. A few secret service organizations encourage the European Community to reduce the international measures which regulate the systems of incorporated protection in mobile phones. Is the federal Council ready to take technical measur-es in order to protect the digital networks of radiotelephony (GSM, NATEL D) against illegal phone-tapping? 2. Is the federal Council ready to intervene through the organizations in charge (CPT, CEE...) in favour of the maintenance, and perhaps the reinforcement of the standard of protection against "A5" phone-tapping, which satisfies the needs of the justice. Unlike the "A5X" standard (see Sunday Times published on the 31.12.1993)... The handies' users will enjoy the most modern coding technique, and they will protect professional secrecy (it will not be the last time that foreign secret services have recorded and published the transcriptions of phone conversations of a future king, or for political reasons). The electronic protection we are talking about does not limit legal phone-tapping from the telephone centrals, or when phone-tapping is ordered by a judge for criminal reasons. The "A5" norms set by the GSM make it difficult or impossible to carry out the decoding operations by using lap-top computers which are sold in stores, if the judge does not deliver a surveillance order. Cosignatories : Aregger, Bezzola, Detting, Fischer-Seegen, Fritschl Oskar,Ernst Muhlemann, Lili Nabholz, Vreni Spoerri, Stamm Luzi, Georg Stucky, Wyss Paul (11) |
Remarks :
1- Who is in charge of the BAKOM
(OFCOM) and the approval of the choice or lack of choice of keys?
20% of employees work in the
Post Office, the rest work in ASCOM.
2- The English case dated May
1993 is either similar to the Koop case or was carried out by an English
official service; but it is internal anyway.
3- The notion of unofficial
phone-tapping is inadequate. Resorting to an independent commission to
have access to protocols and phone-tapping would make it possible to solve
unclear questions.
4- We think that phone-tapping
is reserved to criminals. But Natel D and GSM are not 2 separate things.
5- historically, the numbering
of the protection of "A5" is an algorithm of 256 bits. The A5X or A5/2
project of 56 bits came to the public's attention for one reason : the
Sunday Times article was taken from the New Scientist which got it from
a handies manufacturer who supplies Koweit. It would weaken this firm and
two official phone-tapping organizations.
In 1996, Matracom 9600 acknowledged
the fact that decoding was possible (PC+decoder+digital scanner), which
explained why the police bought security GSM (encoders).
Chronology :
1.93 :New Scientist
31.1.93 : Sunday Times
04.3.93 : Monde du renseignement (the information world)
19.3.93 : National Council
11.6.93 : SKZ
23.7.93 : L'Hebdo
Rhode & Schwarz : possibility of interception the called-calling numbers.
http://www.rsd.de/PRODUKT/22da.htm
http://www.rds.de/presse/default.htm
97 : single station location; direction finding of GSM signals and interception of called-calling numbers :
| no IMSI :
Nr. (HH:MN) : Box erreicht : Text vollständ : Benach (SMS) : |
 |
- Phone-tapping & pocket phones
Phone-tapping while you are walking.
The reduction of the numbering
produced the A5/2, A5/3..A5/7 which were exported to the sensitive countries,
that is to say every country
outside Europe.
1996 will redefine in a more
specific way the choice of each country; in 1995, in the canton of Geneva
to start with, the Swisspoint
(the DECT norm with 500 radioelectric
posts as big as a pack of milk) is a unidirectional phone, with no wire
and no coded digital data,
with a 150 meter range; in 1996,
the satellites will be responsible for leaks from mobile phones (PCN/RNIS)
with a high frequency (1,8 GHz),
when they have listened to the
federal Council or uncovered the bank secrecy (from 1,7 to 2,3 GHz) : Natel
E was created because of
hertzien wave saturation in
the areas located near the border (Geneva, Bale, Zurich...);
N.B.: bi-mode terminals, GSM 900-DCS 1800 such as Natel City can be hybrid (D + City), and can be extended to GSM.
-Interception & GSM
Phone-tapping as you are driving
| Switzerland : (end of 1994)
SWISSCOM:
forecast for 1997 : 2 OMC +
Diax: 1 OMC + 400 BTS
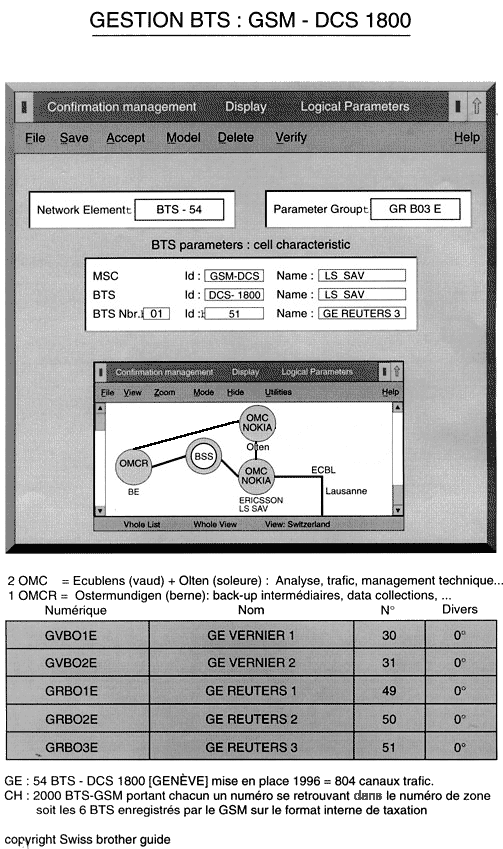
Belgium (Mobistar) : 1 OMC + 3 MSC/VLR/HLR + 600 BTS OMC / supervisor GSM (MSC) : data integrity; networking repdating, databox, maintenance, SIM network, surveillance, performance, analyse, time & data, traffic mesurement, tracing, maps tracing . |
Encoding :
As they reduced encoding keys,
they produced the A5/2, A5/3...A5/7 keys, which were exported to sensitive
countries
(that is to say all countries
but Europe). A5/2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 are inferior to 40 bits.
GSM encoding details are kept secret by the British government in London.
- Data-voice (voice+data) is encoded by mobile phones through an A5 key with a theoretical length of 64 bits and a real length of 40 bits.
The transcoder (encoding /decoding
the voice codes) is set in the BSS (BTS + BSC) : everything is encoded.
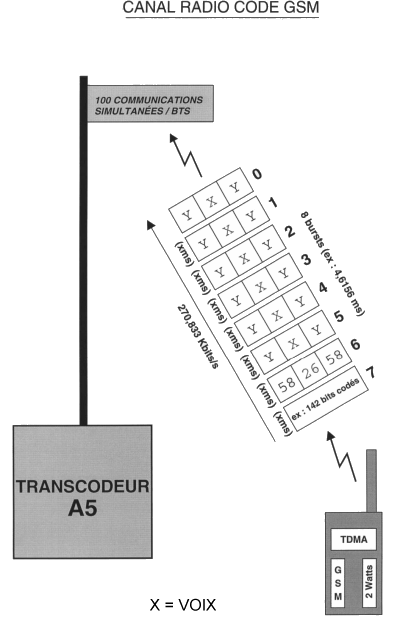
Voice encoding is 13 Kbps, or
270,833 Kbps on the radio channel on the TDMA system
(differential modulation : 11,4,
that is to say 22,8 Kbit/s; the message is sent in bursts divided into
8 coded parts/ms).
The word burst does not mean
anything : indeed, there are different types of bursts :
- channel reject burst;
- securisation burst;
- normal burst (58+26+58 encoded
bits = 142 bits);
- access burst; synchronisation
burst SB;
- frequency correction burst...
Voice and radio channels are encoded.
-Feb.95 : Burst of 557 ms with 116 encoded bits
- Sept.95 : burst of 557 ms with 166 encoded bits
There were some mistakes about
the subject in SWISSCOM magazine, COMTEC in February 1995 (burst of 557
ms with 116 bits)
and in September 1995 (burst
of 557 ms with 166 bits).
Decoding :
It is always, always, always possible to intercept Hertzian transmissions on a computer, and record them through state phone-tapping or otherwise. Only the material makes the difference. All the types of phones available in Switzerland always pass through three types of telephone centrals. The Siemens, Alcatel, Motorola, Matra and Nokia firms, which depend on the GSM group. All these firms work for the military security. Digital scanners and softwares burstsare not enough to get information from the GSM radio transmissions : it is impossible to decode an individual's GSM as the TDMA is a very complex system (multiple accessin time , which makes a mountain of papers as thousands of GSM slot (0, 5769 ms) are sent per message. See "TK & SIM card. The secret service such as the MI 5 had better pretend it is not true by organising a semipublic demonstration which turned out succesfully of GSM decoding by using the usual material.
On the other hand, a good scanner can intercept coming in and going-out calls with handies B and C. A very good scanner gets the whole conversation. A poster displayed in the trains above the handies indicates that confidentiality is not guaranteed. This argument is against the offficial leaks.
As far as D GSM handies are concerned (euro-compatible NT 2ab phone-tapping), a computer and the phone number are necessary to solve the million mathematical operations. SWISSCOM have found the key of the algorithm
Nortel-Matra-Cellular declares to the Science et vie magazine : "it is almost impossible to decode the GSM network communications". Either it is possible, or it is not. The semi-weak or semi-semi weak keys give clues for the analytical attacks, unlike the MC2-PENTAGONE system with three keys made of 16 figures. When you are dealing with cryptography, things are not done by halves, as the crypto SA case showed. The customers buy the product because they think they are protected, and the results of phone-tapping are profitable. The real material of cryptographic coding is used according to three principles : firstly, the material is never used outside its country; secondly, it cannot be exported, thirdly, it is produced by the military services and it is controlled by the intelligence service.
For the trail blazers the complete
digital encoding of voice and data is very difficult and expensive.
Without decoding :
In official phone-tapping, everything depends on the CIT Natel A, B, C, D (GSM) sector. The telephone central Natel-IPMR for the canton of Vaud is located in the Savoy central in Lausanne. Natels A+B concern the telephone central in Préville. In this canton, there are 52 Natel A/B/C stations (or cells). In practice, hundreds of state employees directly listen to the conversations from mobile phones by using the uncoded network.
100% of calls dialled from a
fixed station to a mobile station are monitored on the network. It is not
necessary to monitor from the BSS (BTS + BSC) to the MSC(Savoie in Lausanne).

Thus, the numbering of the PIN or the reconstitution of the intonations of the scrambled voice is superflous to SWISSCOM.
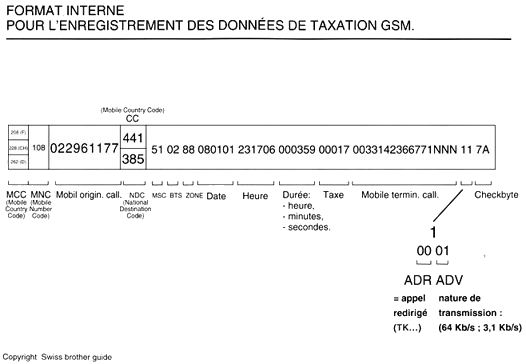
GSM has its own system to make bills (2 different protocols : mobile terminating call). The first three figures of the internal scheme of bill by GSM (example : 208 to France) are different from other systems (MCC : mobile country code). Private operators that do not exist in Switzerland guarantee that there has been no irregular phone-tapping on the GSM Network until 1988.
In 2'000, GSM will automatically
be connected on the satellite
network worlwide in zones which are not covered on the ground
(4'500 simultaneous phone calls
via satellites). Interception
of
the telephone centrals satellite circuits:
In Europ, pnOne gron
ICO (Satelitte Acess Node or
SAN): GERMANY
IRIDIUM: ROME
GLOBALSTAR: FRANCE (Aussaguel)
Without using your phone :
The most interesting is function is "mobile trace". It neither deals with phone-tapping nor location, but with temporary registering of a mobile phone within a country or an area (lists of transit). Indeed, the temporaray file VLR (Visitor Location Register) data is deleted when the subscriber gives up the selected cell. It is then recorded on various stands (VLR memory, LOG, protocols analyser, data base including the number of the cell..., etc). Thecells radius varies from 1 km in the town center to 18 km in the countryside. As far as the urban cell DCS is concerned, (Digital Communications System), the radius varies from 0,1 km to 4 km. Additionally; the VLR information connected on the HLR file (information about the subscriber : the last position is registered)) and on the IMSI file (international identity of the subsciber) can be transferred from one cell to another.
Each VLR manages and registers the location zones. Each subscriber has a VLR address (location in real time) and a single HLR number, so that the automatic location can be made by using a data base. Data is memorized and encoded.
In fact, the teleoperator memorizes the tracks of a mobile phone and it can search it at anytime by consulting the protocols analysers. Every file (subscribers, EIR equipment, etc.) is registered in the MSC or the MOBILCOM central (four of them are in Switzerland, and four in Paris).
Authentification files include the originating call and the equipment used.
Everyday, SWISSCOM SA registers the presence of 30 000 to 40 000 foreigner GSM.
That is to say 1 million calls per month, as well as 8 000 Swiss subscribers (700 000 calls per month). These precise figures show how useful the VLR file is. "Mobile trace" can be very accurate : nationalities, reconstitution of a journey (from 30 to 60 km according to the diameter of the cells). Each GSM permanently records the 6 cells which are in the best position in order to select the best frequency and the best BTS post, which makes irregular phone-tapping harder. There are four levels : perfect way; good way; normal way; bad way.
You can consult "Mobile trace register in cases of faults (various causes : rejected channel, unreceived calls, for instance). As a result, the position of every subscriber is permanently stored.
All this is carried out via OMCR (Operation Maintenance Central Register). The MSC cannot save every documant and resorts to BSC (Base Station Controler) in case of saturation. The BSC can be located 100 km away from the MSC. EX : the Coire-Gäuggeli BSC. A BSC cannot get more than 40 BTS (Base Transceiver Station) . Indeed, BTS are usually placed near the handies' aerial. BTS are switched on for the first time with Racal material in order to load the soft on. One BTS = 100 simultaneous conversations.
It is essential to note that this particular type of phone-tapping is only carried out on GSM when it is switched on and on "pause".
As a temporary conclusion, HLR records, but it does not trace. VLR traces the subscriber in real time.
The hundreds of public officials
who listen to handies demonstrate how easy it is to decipher the message
from a telehone central or any other place connected to a central. The
only problem is how fast the message is processed, as with many other types
of telephonic transmissions.
 |
"Mobile Trace" and transit lists of GSM
Categories and places
Natel B : cantonal location
Natel C : location over 26 cantons
by 900 cells and posts;
Natel D : Swiss location by
500 cells and/or European location (Swiss Natel D)
Natel E : urban tracing, with
about 50 cells per town.
N.B.: several transceivers and cells are used with Natels C and D. From 2 to 10 transceivers are put in every month.
The bips (040/...) for instance, are subjected to the intercellular monitoring of the power of the signal.
Interception & SIM or GSM cards / SWISSCOM cards
Phone-tapping without your phone.
Any personal TELECOM or SIM
card is a personal and unique card (in the form of a credit card or
a microcard) with a microprocessor
containing some information about the subscriber
(data about the subscriber, his/her phone number,
his fast call numbers,...). The card can be inserted in any other GSM phone
equipped
to receive another subscriber and to tax the
card user rather than the phone user. The GSM microprocessor card can hold
200
items of alphanumeric data, 50% of them are recorded by the TELECOM and are related to the data concerning the subscriber.
For instance, they can have access to the file of international identification of the material (IMEI, ...). The card is usually used with a key which generates an A8 algorithm. The chip holds the subscriber's identification (A8 and A3) in order to make a black list.
The A3 encoding is set in a file AVC, HLR and
VLR, and at the other end of the network on the SIM card. The GSM algorithms
are always
checked twice. The A8 card of the SIM card
is also set up in the IMSI file (International Mobile Suscriber Identity).The
new SIM/Data card
is called the Natel Sicap card (processor
on a SIM card). With this card, you can pay for a bill, load a credit,
book a ticket...etc.
The PCMCIA can hold a scrambling data algorithm.
The transmissions are monitored on a channel which is controlled; yet,
this precaution
is useless as the TELECOM carry out direct
phone-tapping on the uncoded network. When they carry out tests such as
the TIME SLOT,
technicians directly monitor the GSM conversations.
TIME SLOT controls conversations.
When shall we have the complete chip card,
containing your story, your check up (in Germany, there are already 70
million chip cards
containing the patient's prescriptions), your
bank account and your trips? Sweden is the typical example
(an omniscient number : small offences, debts...).
Quite soon, the SIM card will be integrated into the phones in the hotels.
It will be possible to check the bill details.
As far as the GSM data transmissions are concerned,
the GPS DATA-FAX-Modem cards plus an interface make it possible to have
access
to Thernet, Internet (world network), Novell
(Software), Token-Ring or Twin Axe connected to the RNIS. The telephone
centrals register
a minimum of information for these outputs.
There is a problem. Indeed, following the example of legitimate blacklists
sush as the TDO
(table of denial orders), the SIM cards also
have a blacklist, in order to deal with the people who are registered on
the F.A.O,
(Official Advice Form) in the bankruptcy section,
or to operate automatic and vocal localizations through the central.
Thus, even when it is used in roaming, the
card which is used in foreign countries is always under control (MCA*TKG,
Natel central).
The PIN numbers are useless (personal identification
with 4 figures).
To decode GSM phone calls outside Unisource
territory (first circle : the Netherlands, Sweden and Switzerland), to
interrogate the
computers' memory and to spy from a distance,
all this is part of SWISSBROTHER's ambitions, by selecting the so-called
suspect
at the time when the card is created. These
cards may have hidden failings.
As far as transmitters, switchboards and mobile phones are concerned, the Swiss security services always have the last word. Even if they pretend the contrary.
Everything is dealt with in the telephone centrals.
Unisource Mobile (Stockholm) will be more and more important.